
Bariatric Surgery Comparison Chart
| Modality of Weight Loss |
Restrictive and Malabsorptive (stomach and intestines) |
Restrictive (stomach only) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Operation | Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery | Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy | Lap-Band Surgical Procedure |
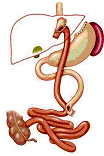
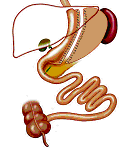
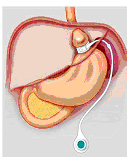
| Anatomy | Small 1 ounce pouch (20-30cc) connected to the small intestine. Food and digestive juices are separated for 3-5 feet. | Long narrow vertical pouch measuring 2-3 oz (60-100cc). Identical to the duodenal switch pouch but smaller. No intestinal bypass performed. | An adjustable silicone ring (band) is placed around the top part of the stomach creating a small 1-2 ounce (15-30cc) pouch. |
|
|
|
|
| Mechanism |
|
|
|
| Weight Loss United States Average statistical loss at 10 years |
|
|
|
| Long Term Dietary Modification (Excessive carbohydrate/high calorie intake will defeat all procedures) |
|
|
|
| Nutritional Supplements Needed (Lifetime) |
|
|
|
| Potential Problems |
|
|
|
| Hospital Stay | 2-3 days | 1-2 days | Overnight (<1 day) |
| Time off Work | 2-3 weeks | 1-2 weeks | 1 week |
| Operating Time | 2 hours | 1.5 hours | 1 hour |
| Recommendation | Most effective for patients with a BMI of 35-55 kg/m2 and those with a "sweet-tooth". Virtually all insurance companies will authorize this procedure. | Utilized for high risk or very heavy (BMI > 60 kg/m2) patients as a "first-stage" procedure. Very low complication rate due to quicker OR time and no intestinal bypass performed. Insurance companies will authorize this procedure in select patients. | Best for patients who enjoy participating in an exercise program and are more disciplined in following dietary restrictions. Many insurance companies will NOT authorize this procedure. |

